
大气污染控制研究室主要针对国民经济发展中出现的重大大气环境问题,基于吸附、催化、纳米等技术,着重开展典型大气污染物(VOCs、含N污染物、CO、CO2等)纳米催化净化功能材料构建、应用技术与方法的研究,以实现气态污染物绿色、低耗、高效、高选择性的去除与资源转化。课题组现有教授1人,讲师1人。近5年承担多项国家、省部级以及企业委托项目。发表SCI论文百余篇,获授权专利7项。
主要研究方向:(1) 环境多功能材料的构建,(2) 气态污染物控制技术开发,(3) 表面反应过程动态原位谱学研究, (4)整体催化剂的开发与应用。
Aiming at the important problems of air pollution along with the development of the national economy, our laboratory focuses on the research and application of nano-catalysis for the removal of air pollutants (VOCs, NOx, CO2, etc.) based on the adsorption, catalysis and nanotechnology. The laboratory currently has 1 professor, 1 associate professor and 1 lecturer, and has undertaken lots of national, provincial and enterprise cooperation projects in the last 5 years. More than 100 academic articles have been published in SCI journals and 7 China patents for inventions have been authorized.
The main research fields include: (1) Environmental Multi-function Materials, (2) Gaseous Pollutant Control Technology, (3) In situ Spectroscopy of Surface Reaction, (4) Development of Monolithic Catalysts.
代表性成果
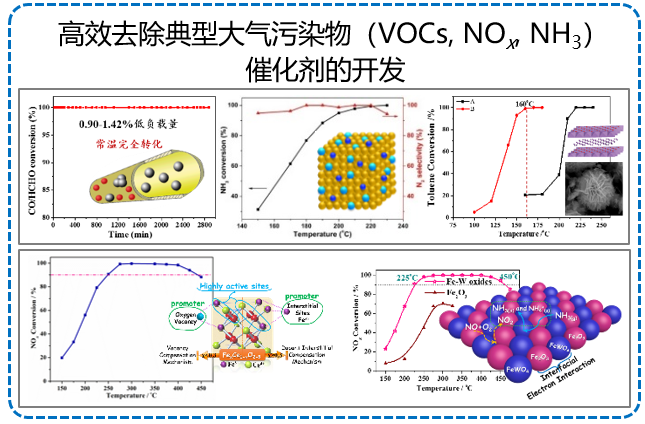
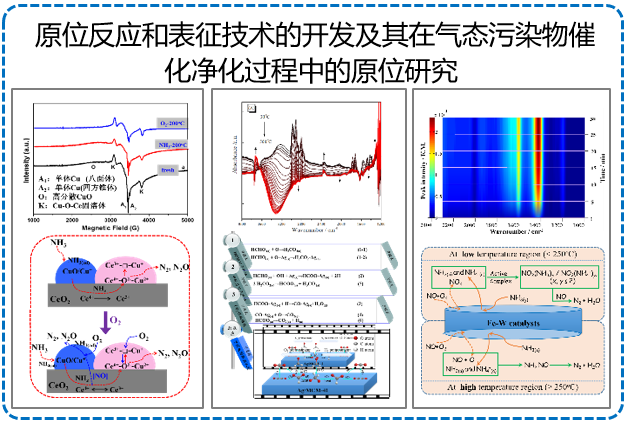
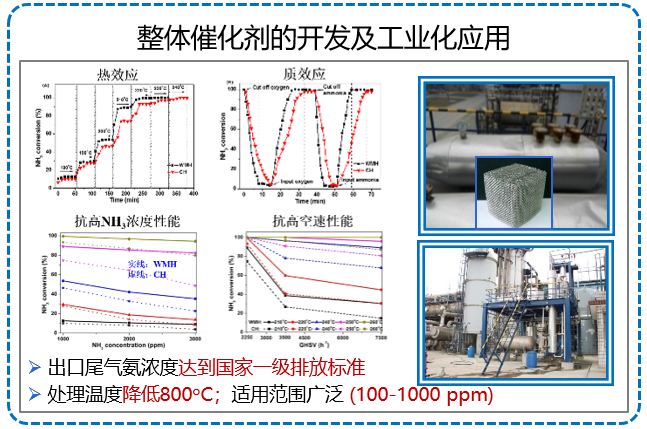
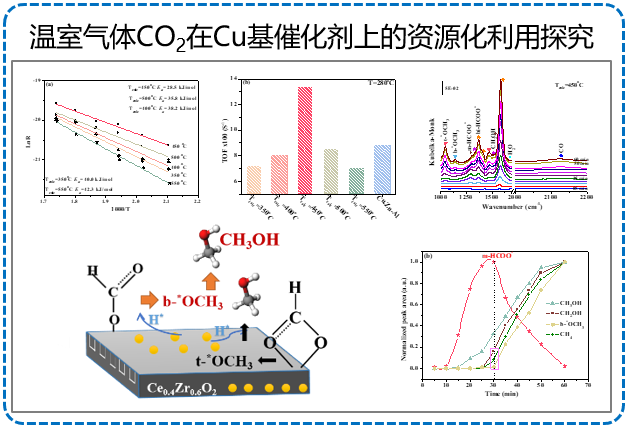
代表论文
1. Evolution and enhancement of the oxygen cycle in the catalytic performance of total toluene oxidation over manganese-based catalysts, J. Catal., 380 (2019) 21-31.
2. Revealing the highly catalytic performance of spinel CoMn2O4 for toluene oxidation: involvement and replenishment of oxygen species using in situ designed-TP techniques, ACS Catal., 9 (2019) 6698-6710.
3. Study of synergistic effect between CuO and CeO2 over CuO@CeO2 core-shell nanocomposites for NH3-SCO, Catal. Sci. Technol., 9 (2019) 2968-2981.
4. HCHO oxidation over highly dispersed Au nanoparticles supported on mesoporous silica with superior activity and stability, Catal. Today, 327 (2019) 210-219.
5. Mechanistic study of FeW mixed oxides to the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3: in situ DRIFTS and MS. Catal. Today, 307 (2018) 35-40.
6. Adsorption and surface reaction pathway of NH3 selective catalytic oxidation over different Cu-Ce-Zr catalysts. Appl. Surf. Sci., 447 (2018) 40-48.
7. Study of SO2 effect on selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 over Fe/CNTs: the change of reaction route. Catal. Today, 307 (2018) 2-11.
8. Mechanistic investigation into the effect of sulfuration on the FeW catalysts for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 9 (2017) 7017-7028.
9. Superior performance of Fe1-xWxOδ for the selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3: Interaction between Fe and W, Environ. Sci. Technol., 50 (2016) 13511-1351
10. Insight into the mesoporous FexCe1-xO2-δ catalysts for selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3: Regulable structure and activity, J. Catal. 338 (2016) 56-67.
11. Role of different coordinated Cu and reactive oxygen species on the highly active Cu–Ce–Zr mixed oxides in NH3-SCO: a combined in situ EPR and O2-TPD approach, Catal. Sci. Technol., 385 (2016) 4491-4502.
12. Highly dispersed Fe2O3 on carbon nanotubes for low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NO with NH3, Chem. Commun., 51(5) (2015) 956-958.
13. Role of the Al chemical environment in the formation of silver species and its CO oxidation activity, J. Catal., 321 (2015) 113-122.